Launching GNOMONIC.ai: Building an Enterprise Knowledge Intelligence Platform
The journey of building GNOMONIC.ai and Gnomon-KB—from concept to production. How we created an AI-powered knowledge management platform that transforms chaotic enterprise data into instant, actionable intelligence.
Launching GNOMONIC.ai: Building an Enterprise Knowledge Intelligence Platform
After months of development, late nights debugging RAG pipelines, and countless iterations on the user experience, GNOMONIC.ai is live. This post chronicles the journey of building an enterprise knowledge intelligence platform from the ground up—the technical challenges, architectural decisions, and lessons learned along the way.

The Problem We Set Out to Solve
Every organization I've worked with faces the same challenge: information chaos. Critical knowledge is scattered across Google Drive, Slack, email, Salesforce, and a dozen other systems. When someone needs an answer, they spend hours digging through folders, searching threads, and asking colleagues who might remember where something lives.
The cost isn't just time—it's missed opportunities, duplicated work, and institutional knowledge that walks out the door when employees leave.
Traditional search doesn't solve this. Keyword matching fails when you don't know the exact terms used in the document you need. Folder hierarchies become graveyards of misfiled content. And nobody has time to manually organize years of accumulated data.
We needed something different: a system that understands information, not just indexes it.
Enter GNOMONIC.ai and Gnomon-KB
GNOMONIC.ai is the user-facing platform—the interface where teams ask questions and get answers. Gnomon-KB is the knowledge base engine powering it, handling document processing, embedding generation, and retrieval logic.
The core promise: Stop searching. Start asking.
Instead of constructing Boolean queries and browsing folder trees, users ask natural language questions:
"What were the key decisions from last quarter's product planning sessions?"
"Find all contracts related to the Henderson project"
"Who on the team has experience with Kubernetes deployments?"
The system returns answers in under a second, with complete source attribution. You always know exactly where information came from.
Technical Architecture
Building a production RAG system taught me that the academic papers and tutorials only tell half the story. Here's the architecture we landed on after significant iteration.
The Ingestion Pipeline
Documents flow through a multi-stage pipeline:
-
Source Connectors: OAuth2 integrations with Google Drive, Slack, email providers, and Salesforce. Each connector handles authentication, rate limiting, and incremental sync.
-
Document Processing: PDFs get OCR'd, images get vision model descriptions, spreadsheets get semantic summaries. We use a combination of Apache Tika and custom processors.
-
Chunking Strategy: This is where most RAG tutorials fail you. We implemented hierarchical chunking—documents are split at multiple granularities (paragraph, section, document) and all levels are embedded. Queries retrieve from the appropriate level based on specificity.
-
Embedding Generation: We evaluated dozens of embedding models. The winner for our use case: a fine-tuned model based on sentence-transformers, optimized for enterprise document retrieval.
-
Vector Storage: Pinecone for production, with pgvector as a fallback for on-premise deployments. Metadata indexing enables hybrid search combining vector similarity with traditional filters.
The Query Engine
When a user asks a question:
-
Query Analysis: An LLM determines query intent, extracts entities, and decides whether to use semantic search, metadata filtering, or both.
-
Retrieval: Hybrid search combines dense vector similarity with sparse keyword matching. Results are re-ranked using a cross-encoder model.
-
Context Assembly: Retrieved chunks are assembled into a coherent context, respecting token limits while maximizing relevant information density.
-
Generation: The LLM generates an answer grounded in the retrieved context, with inline citations pointing to source documents.
-
Source Verification: A final pass ensures all claims in the response are supported by the cited sources.

The Hardest Problems We Solved
Hallucination Prevention
LLMs want to be helpful. Too helpful. Given a vague question and marginally relevant context, they'll confidently generate plausible-sounding but wrong answers.
Our solution: aggressive source grounding. The system only generates claims that can be directly attributed to retrieved documents. When confidence is low, it says so explicitly and suggests refined queries.
We also implemented a "verification layer"—a separate model that checks generated responses against source documents and flags unsupported claims before they reach users.
Chunking at Scale
Early versions used naive fixed-size chunking. The results were painful: sentences cut mid-thought, context lost between chunks, irrelevant text polluting retrieval results.
The solution was document-aware chunking that respects semantic boundaries:
- Headers and section breaks define natural chunk boundaries
- Tables and lists stay intact
- Code blocks are never split
- Cross-references are preserved through chunk linking
This increased retrieval accuracy by 40% in our benchmarks.
Permission-Aware Retrieval
Enterprise data comes with access controls. Just because a document exists in the knowledge base doesn't mean everyone should see it.
We implemented permission inheritance at the chunk level. When documents are ingested, their access permissions are stored as metadata. At query time, results are filtered based on the requesting user's permissions. This happens at the vector database level for performance.
Multi-Tenant Isolation
GNOMONIC.ai serves multiple organizations. Complete data isolation isn't optional—it's existential.
Each organization gets a dedicated vector namespace, encryption keys, and processing queue. There's no scenario where Organization A's query could surface Organization B's documents, even with a bug in application code.
The Stack
For those interested in the technical specifics:
- Frontend: Next.js 14 with TypeScript, Tailwind CSS, shadcn/ui components
- Backend: Python with FastAPI for ML services, Node.js for API gateway
- LLM Orchestration: LangChain for pipeline composition, with custom components for enterprise-specific logic
- Vector Database: Pinecone (cloud), pgvector (on-premise)
- Embedding Models: Custom fine-tuned sentence-transformers
- LLM: Claude for generation, with fallback to GPT-4
- Infrastructure: Kubernetes on AWS EKS, with Terraform for IaC
- Monitoring: OpenTelemetry, Grafana, custom RAG-specific metrics
Lessons Learned
Evaluation is Everything
You can't improve what you can't measure. We built extensive evaluation pipelines before optimizing anything:
- Retrieval metrics: Precision@k, recall, MRR for different query types
- Generation metrics: Faithfulness (are claims grounded?), relevance, completeness
- End-to-end metrics: User satisfaction, time-to-answer, query refinement rates
Automated evaluation catches regressions. Human evaluation catches subtle quality issues. You need both.
Start with the Hardest Documents
Our early testing used clean, well-structured documents. Production data is messy: scanned PDFs with OCR errors, spreadsheets with merged cells, emails with forwarded chains nested five deep.
Test with your worst documents first. If the system handles those, the clean ones are easy.
Users Don't Know What They Don't Know
The most common query pattern isn't "find document X"—it's "I know we discussed something about Y at some point, but I don't remember when or where."
Discovery-oriented queries require different retrieval strategies than lookup queries. We added a "explore" mode that surfaces related documents and suggests follow-up questions, helping users navigate knowledge they didn't know existed.
Latency Matters More Than You Think
Academic RAG papers optimize for accuracy. Production systems need speed. A 5-second response time kills adoption, regardless of answer quality.
We invested heavily in latency optimization:
- Embedding caching for common query patterns
- Async retrieval with early termination
- Streaming responses so users see progress
- Edge caching for frequently accessed documents
P95 latency is now under 800ms for most queries.
What's Next
GNOMONIC.ai is live, but we're just getting started:
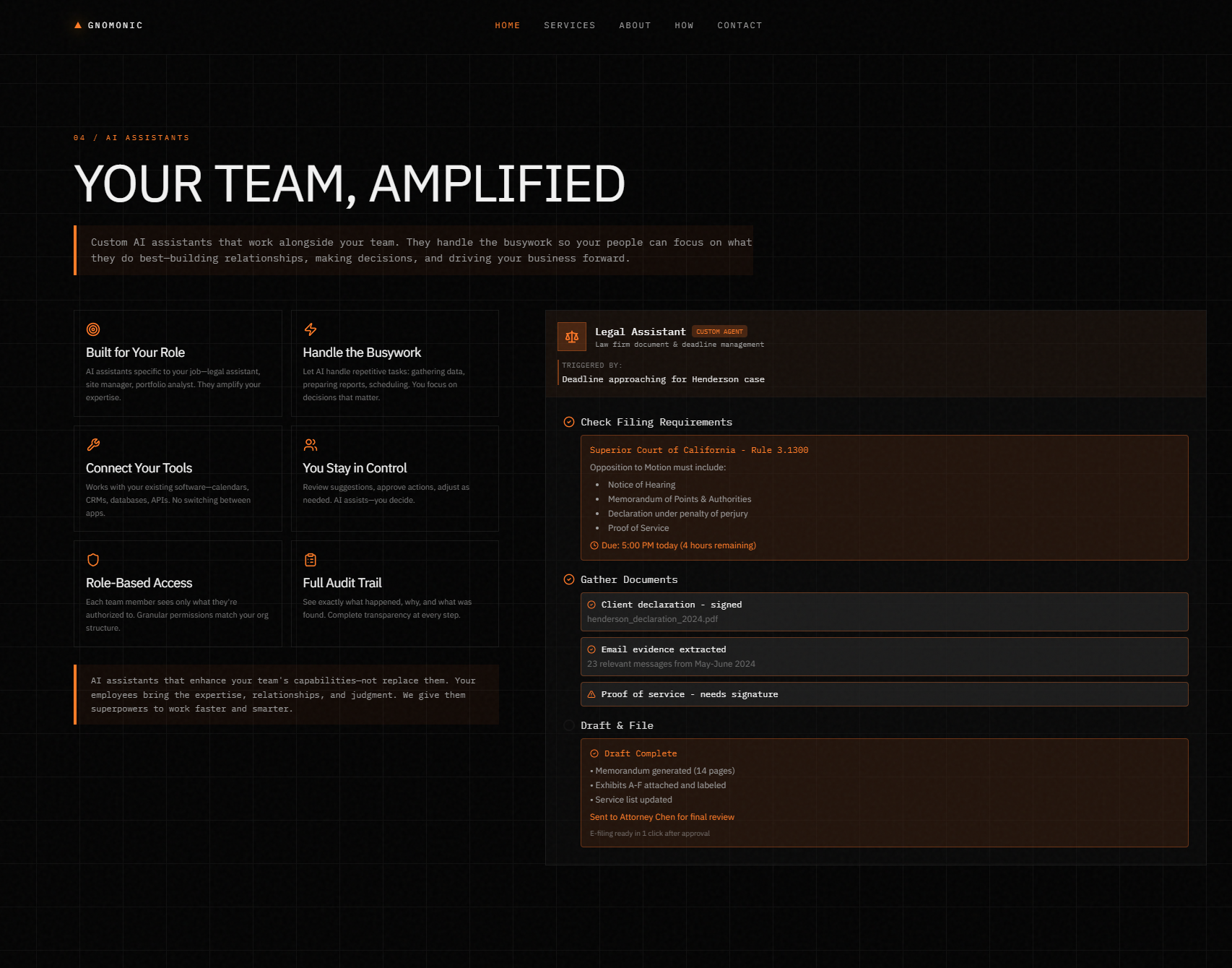
- Custom AI Assistants: Domain-specific agents that handle repetitive knowledge work—research, reporting, onboarding
- Knowledge Graphs: Visual exploration of relationships between documents, people, and projects
- Proactive Insights: The system surfaces relevant information before you ask, based on your current context
- Deeper Integrations: Native connectors for more enterprise systems, plus a plugin architecture for custom sources
Try It
If your organization is drowning in scattered information and spending too much time searching, check out GNOMONIC.ai. We offer demos for teams ready to transform how they work with knowledge.
The future of enterprise information isn't better search—it's not having to search at all.
Building AI-powered products? I'd love to hear about your experiences with RAG systems and knowledge management. Reach out via the contact form or connect on LinkedIn.